Quadriceps Strain
Quadriceps strain, or a pulled quad muscle is a common injury in sports. As with most muscle strains, it can occur with any activity that requires explosive contraction of the muscles.Quad strains, much like hamstring strains, can become chronic nagging injuries if not treated correctly. Read on to learn more about this sports injury, how it occurs, and how it should be treated and prevented.
The Quadriceps
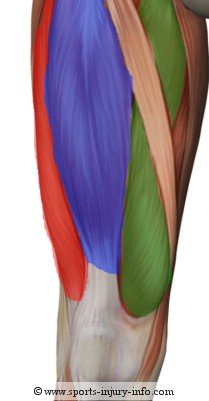
The vastus muscles all attach on the proximal femur, and run down the front of the leg, inserting on the patella through the quadriceps tendon. The rectus femoris attaches above the hip joint on the anterior inferior iliac spine, and courses down the leg inserting into the patella, again through the quadriceps tendon.
All of the quadriceps muscles help to extend the knee, and the rectus femoris muscle helps to flex the hip as well.
The rectus femoris is one of the most commonly strained quadriceps muscles, and may also be involved in hip flexor strains as well.
What is a Quadriceps Strain?
A quadriceps strain is a tearing of the muscle fibers in one of the four quadriceps muscle, most commonly occuring in the rectus femoris.This injury occurs with explosive contraction of the muscle, often when trying to change directions, jumping, or taking off to run.
Quad injury is graded using the 1-3 scale, with grade 1 strains being the least severe, and grade 3 being the worst.
Depending on the severity of the strain, you may be able to feel a defect in the muscle, or a hole where the tear is.
Symptoms
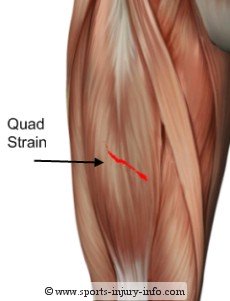
The most common symptom of a quadriceps strain is pain. It is usually acute in nature, occuring immediately after the injury. You generally know as soon as it happens when you strain your quad.
There may be swelling around the site of injury, and you may have some discoloration around the injury site as well. If the tear is large, and there is a lot of bleeding, swelling may spread throughout the entire thigh.
Muscle spasm, or knots in the muscle, are also very common symptoms of a quad injury.
Treatment

It is important to let this tissue heal without increasing stresses on the muscle, and to control the inflammation process early on.As the muscle heals, you can begin to start gently stretching the muscles, and working towards regaining your strength.
Because the quad muscles are large muscles and are made up of many many fibers all surrounded by connective tissue, when the muscle is strained and heals through scar formation, this tissue can cause restrictions in flexibility, and is more susceptible to re-injury.
To treat a quadriceps strain properly, and to prevent re-injury, you should have some type of rehabilitation. This is important to return normal flexibility, strength, and endurance, and to monitor scar formation.
Most soft tissue injuries heal within several weeks. You should be able to return to normal activities anywhere from 2-6 weeks, depending on the severity of your injury.
Prevention
Preventing quadriceps strains involves a good warm up and stretching program prior to activities, as well as making sure you are properly conditioned for your sports activities.Preventing re-injury revolves around making sure you allow the first injury to heal before returning to sports, and going through rehabilitation to restore your strength and flexibility.
Summary
Quadriceps injury is very common in sports. If treated correctly, you can usually recover within 2-6 weeks, and return to your sport. If not treated appropriately, it can become a nagging injury with a high recurrance rate. Treatment revolves around rest, ice, compression, and elevation initially, followed by rehabilitation to restore flexibility and strength.Didn't find what you were looking for? Search SII for more information...
Running Pain Solutions
Written for Runners by a runner, you'll learn a holistic approach to improving mobility, restoring normal movement and muscle activation patterns, and restoring the body and mind connection.
This Kindle Book contains a step by step program to keep you running pain free. Included are detailed instructions and illustrations for exercises to improve mobility, balance, neuromuscular control, strength and endurance. Only $7.49!
Get Your Copy Today!









